Understanding the Heart’s Circulatory System: Pathways of Life
The heart, a remarkable organ, serves as the engine of our circulatory system. Its primary role is to pump blood throughout the body, delivering essential nutrients and oxygen while removing waste products. Understanding how this intricate system works can shed light on how to maintain a healthy heart and overall well-being.
The Basics of the Circulatory System
The circulatory system, also known as the cardiovascular system, consists of the heart and a network of blood vessels, including arteries, veins, and capillaries. It is responsible for transporting blood throughout the body, ensuring that organs receive the oxygen and nutrients they need to function properly.
The Anatomy of the Heart
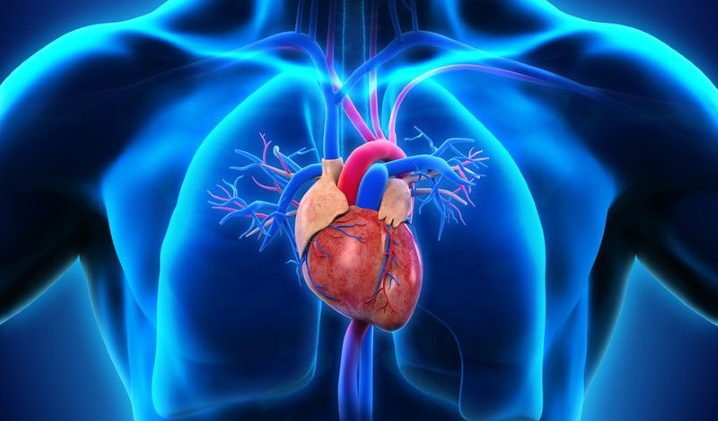
The heart is divided into four main chambers: the right atrium, right ventricle, left atrium, and left ventricle. Each chamber plays a vital role in the circulation of blood:
- Right Atrium: Receives deoxygenated blood from the body through the superior and inferior vena cavae.
- Right Ventricle: Pumps the deoxygenated blood to the lungs via the pulmonary artery for oxygenation.
- Left Atrium: Receives oxygenated blood from the lungs through the pulmonary veins.
- Left Ventricle: Pumps oxygenated blood to the rest of the body through the aorta.
How Blood Circulates: The Pathway of Blood Flow
The circulatory system operates in two primary circuits: the pulmonary circuit and the systemic circuit.
- Pulmonary Circuit: This pathway carries deoxygenated blood from the right side of the heart to the lungs, where carbon dioxide is exchanged for oxygen. The oxygen-rich blood then returns to the left side of the heart.
- Systemic Circuit: This pathway distributes oxygenated blood from the left side of the heart to the rest of the body. After delivering oxygen and nutrients, blood returns to the right side of the heart, completing the cycle.
Understanding Blood Vessels
Blood vessels are classified into three main types, each with unique functions:
- Arteries: Carry oxygen-rich blood away from the heart to the tissues. They have thick, elastic walls to withstand high pressure.
- Veins: Return deoxygenated blood back to the heart. They have thinner walls than arteries and often contain valves to prevent backflow.
- Capillaries: These tiny vessels connect arteries and veins, facilitating the exchange of oxygen, carbon dioxide, nutrients, and waste products between blood and tissues.
The Heart’s Electrical System
The heart has its own electrical system that regulates the heartbeat. The sinoatrial (SA) node, located in the right atrium, acts as the natural pacemaker, generating electrical impulses that cause the heart to contract and pump blood. Understanding the heart’s electrical system is essential for recognizing arrhythmias and other heart rhythm disorders.
Factors Affecting Circulatory Health
Maintaining a healthy circulatory system is crucial for overall heart health. Several factors can impact this system:
- Diet: A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins supports cardiovascular health.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity strengthens the heart muscle and improves circulation.
- Smoking: Tobacco use is a significant risk factor for cardiovascular disease, as it damages blood vessels and reduces oxygen levels.
- Stress: Chronic stress can lead to high blood pressure and other cardiovascular issues. Stress management techniques can help mitigate these effects.
- Genetics: Family history can play a role in an individual’s risk for heart disease. Knowing your family’s health history can help guide preventive measures.
Signs of Circulatory Issues
Being aware of the signs of circulatory problems is essential for early intervention. Common symptoms may include:
- Shortness of breath
- Chest pain or discomfort
- Fatigue or weakness
- Swelling in the legs, ankles, or feet
- Irregular heartbeat
If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to consult a healthcare provider for a thorough evaluation.
Preventive Measures for Heart Health
Taking proactive steps can help maintain a healthy circulatory system:
- Regular Check-ups: Routine visits to your healthcare provider can help monitor blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and overall heart health.
- Healthy Lifestyle Choices: Incorporate a balanced diet, regular exercise, and stress management techniques into your daily routine.
- Avoid Tobacco: Quitting smoking can significantly reduce your risk of cardiovascular disease.
- Limit Alcohol: Moderation is key; excessive alcohol consumption can lead to high blood pressure and other heart-related issues.
Conclusion
Understanding the heart’s circulatory system is fundamental to recognizing the importance of cardiovascular health. By taking proactive measures and being aware of the factors that impact heart health, you can help ensure your heart remains strong and efficient throughout your life.
Disclaimer: This blog post is intended for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Always consult a healthcare professional for medical concerns and before making any changes to your health regimen.
Disclaimer: This article is for educational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a qualified healthcare professional.
